Jordanian Annexation Of The West Bank on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Jordanian annexation of the West Bank formally occurred on 24 April 1950, after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, during which 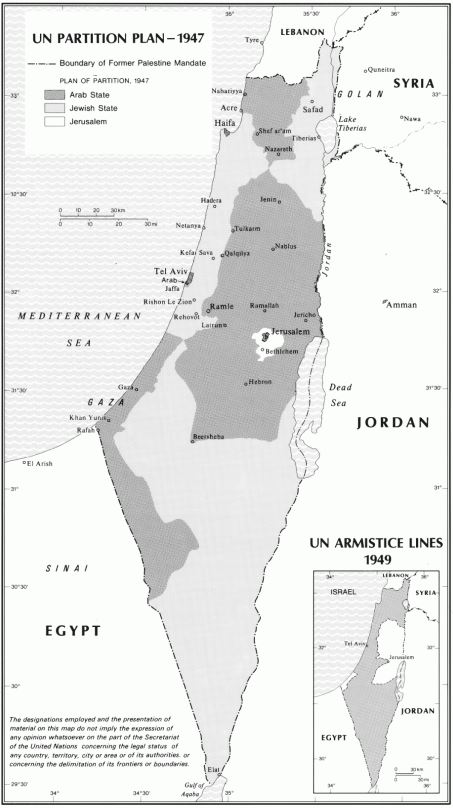
File:Porat Yosef attack.jpg, Arab Legionnaires attacking
Hussein Move May Snag Peace Initiative
- published on
Hussein Muddies Mideast Waters
- published on
King Hussein's Bombshell
- published on
Disengagement from the West Bank
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jordanian occupation of the West Bank History of Palestine (region) 20th century in Jerusalem Israel–Jordan relations Military occupation Annexation of the West Bank Annexation of the West Bank Annexation of the West Bank States and territories established in 1948 States and territories disestablished in 1967 Annexation of the West Bank Annexation of the West Bank History of the West Bank West Bank Governorate 1988 in Jordan Palestine Liberation Organization Israeli–Palestinian conflict Arab–Israeli conflict July 1988 events in Asia 1940s in the West Bank Governorate 1950s in the West Bank Governorate 1960s in the West Bank Governorate 1940s in Jerusalem 1950s in Jerusalem 1960s in Jerusalem Annexation
Transjordan Transjordan may refer to:
* Transjordan (region), an area to the east of the Jordan River
* Oultrejordain, a Crusader lordship (1118–1187), also called Transjordan
* Emirate of Transjordan, British protectorate (1921–1946)
* Hashemite Kingdom of ...
occupied territory that had previously been part of Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
Raphael Israeli, Jerusalem divided: the armistice regime, 1947–1967, Volume 23 of Cass series – Israeli history, politics, and society, Psychology Press, 2002, p. 23. and had been earmarked by the UN General Assembly Resolution 181
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Re ...
of 29 November 1947 for an independent Arab state to be established there alongside a Jewish state mainly to its west. The annexation tripled the population of Transjordan, from 400,000 to 1,300,000, and the country became a dualistic society with the Palestinian and Transjordanian communities remaining distinct.
During the war, Jordan's Arab Legion
The Arab Legion () was the police force, then regular army of the Emirate of Transjordan, a British protectorate, in the early part of the 20th century, and then of independent Jordan, with a final Arabization of its command taking place in 1 ...
took control of territory on the western side of the Jordan River, including the cities of Jericho, Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
, Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after Eas ...
, Nablus and eastern Jerusalem, including the Old City. Following the end of hostilities, the area that remained under Jordanian control became known as the West Bank.
During the December 1948 Jericho Conference
The Jericho Conference ( ar, مؤتمر أريحا) was held in December 1948 to decide the future of the portion of Palestine that was held by Jordan at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, led by Sheikh Muhammad Ali Ja'abari. Pro-Jordanian p ...
, hundreds of Palestinian notables in the West Bank gathered, accepted Jordanian rule and recognized Abdullah
Abdullah may refer to:
* Abdullah (name), a list of people with the given name or surname
* Abdullah, Kargı, Turkey, a village
* ''Abdullah'' (film), a 1980 Bollywood film directed by Sanjay Khan
* '' Abdullah: The Final Witness'', a 2015 Pakis ...
as ruler. The West Bank was formally annexed on 24 April 1950, but the annexation was widely considered as illegal and void by most of the international community. A month afterwards, the Arab League declared that they viewed the area "annexed by Jordan as a trust in its hands until the Palestine case is fully solved in the interests of its inhabitants." Recognition of Jordan's declaration of annexation was granted only by the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, with disputed claims that Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
also recognized the annexation.
When Jordan transferred its full citizenship rights to the residents of the West Bank, the annexation more than doubled the population of Jordan. The naturalized Palestinians enjoyed equal opportunities in all sectors of the state without discrimination, and they were given half of the seats of the Jordanian parliament
The Parliament of Jordan ( ar, مجلس الأمة ') is the bicameral Jordanian national assembly. Established by the 1952 Constitution, the legislature consists of two houses: the Senate ( ar, مجلس الأعيان ''Majlis Al-Aayan'') ...
.
After Jordan lost the West Bank to Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Ju ...
, the Palestinians there remained Jordanian citizens until Jordan renounced claims to and severed administrative ties with the territory in 1988.

Background
Partition and 1947/8 diplomacy
Prior to hostilities in 1948, Palestine (modern-dayWest Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza.. ...
and Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
) had been administered by the British Empire pursuant to the Mandate for Palestine, having captured it from the Ottomans in 1917. The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, as custodians of the land, implemented the land tenure laws in Palestine, which it had inherited from the Ottoman (as defined in the Ottoman Land Code of 1858
The Ottoman Land Code of 1858 (recorded as 1274 in the Islamic calendar) was the beginning of a systematic land reform programme during the Tanzimat (reform) period of the Ottoman Empire in the second half of the 19th century. This was followed b ...
), applying these laws to both Arab and Jewish tenants, legal or otherwise. Toward the expiration of the British Mandate, Arabs aspired for independence and self-determination, as did the Jews of the country.
On 29 November 1947 the UN General Assembly passed Resolution 181
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Re ...
which envisaged the division of Palestine into three parts: an Arab State, a Jewish State and the City of Jerusalem. The proposed Arab State would include the central and part of western Galilee, with the town of Acre, the hill country of Samaria and Judea, an enclave at Jaffa, and the southern coast stretching from north of Isdud (now Ashdod) and encompassing what is now the Gaza Strip, with a section of desert along the Egyptian border. The proposed Jewish State would include the fertile Eastern Galilee, the Coastal Plain, stretching from Haifa to Rehovot and most of the Negev desert. The Jerusalem Corpus Separatum was to include Bethlehem and the surrounding areas. The proposed Jewish State covered 56.47% of Mandatory Palestine (excluding Jerusalem) with a population of 498,000 Jews and 325,000 Arabs while the proposed Arab State covered 43.53% of Mandatory Palestine (excluding Jerusalem), with 807,000 Arab inhabitants and 10,000 Jewish inhabitants and in Jerusalem, an international trusteeship regime where the population was 100,000 Jews and 105,000 Arabs.
In March 1948, the British Cabinet had agreed that the civil and military authorities in Palestine should make no effort to oppose the setting up of a Jewish State or a move into Palestine from Transjordan.
The United States, together with the United Kingdom favoured the annexation by Transjordan. The UK preferred to permit King Abdullah to annex the territory at the earliest date, while the United States preferred to wait until after the conclusion of the Palestine Conciliation Commission brokered negotiations.
Entry of Transjordan forces into Mandate Palestine
Following theEnd of the British Mandate for Palestine
The end of the British Mandate for Palestine was formally made by way of the Palestine bill of 29 April 1948. A public statement prepared by the Colonial and Foreign offices confirmed termination of British responsibility for the administration o ...
and Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
's declaration of independence on 14 May 1948, the Arab Legion
The Arab Legion () was the police force, then regular army of the Emirate of Transjordan, a British protectorate, in the early part of the 20th century, and then of independent Jordan, with a final Arabization of its command taking place in 1 ...
, under the leadership of Sir John Bagot Glubb, known as Glubb Pasha
Lieutenant-General Sir John Bagot Glubb, KCB, CMG, DSO, OBE, MC, KStJ, KPM (16 April 1897 – 17 March 1986), known as Glubb Pasha, was a British soldier, scholar, and author, who led and trained Transjordan's Arab Legion between 1939 a ...
, was ordered to enter Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
and secure the UN designated Arab area.
Armistice
By the end of the war, Jordanian forces had control over the West Bank, including East Jerusalem. On 3 April 1949, Israel and Jordan signed an armistice agreement. The main points included: * Jordanian forces remained in most positions they held in theWest Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, including East Jerusalem and the Old City.
* Jordan withdrew its forces from its front posts overlooking the Sharon plain
The Sharon plain ( ''HaSharon Arabic: سهل شارون Sahel Sharon'') is the central section of the Israeli coastal plain. The plain lies between the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Samarian Hills, to the east. It stretches from Nahal T ...
. In return, Israel agreed to allow Jordanian forces to take over positions in the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
previously held by Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
i forces.
* A Special Committee was to be formed to make arrangements for safe movement of traffic between Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and the Mount Scopus
Mount Scopus ( he, הַר הַצּוֹפִים ', "Mount of the Watchmen/ Sentinels"; ar, جبل المشارف ', lit. "Mount Lookout", or ' "Mount of the Scene/Burial Site", or ) is a mountain (elevation: above sea level) in northeast Je ...
campus of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, along the Latrun
Latrun ( he, לטרון, ''Latrun''; ar, اللطرون, ''al-Latrun'') is a strategic hilltop in the Latrun salient in the Ayalon Valley, and a depopulated Palestinian village. It overlooks the road between Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, 25 kilometers ...
-Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
Highway, free access to the Holy Places
Sacred space, sacred ground, sacred place, sacred temple, holy ground, or holy place refers to a location which is deemed to be sacred or hallowed. The sacredness of a natural feature may accrue through tradition or be granted through a bless ...
, and other matters. The committee was never formed, and access to the Holy Places was denied to Israelis.
The remainder of the area designated as part of an Arab state under the UN Partition Plan was partly occupied by Egypt (Gaza Strip), partly occupied and annexed by Israel (West Negev, West Galilee, Jaffa). The intended international enclave of Jerusalem was divided between Israel and Jordan.
Jordanian occupation and annexation
The road to annexation
After the invasion, Jordan began making moves to perpetuate the Jordanian occupation over the Arab part of Palestine. King Abdullah appointed governors on his behalf in the Arab cities of Ramallah,Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after Eas ...
, Nablus, Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
, Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
and the Arab controlled part of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, that were captured by Legion in the invasion. These governors were mostly Palestinians (including Aref al-Aref
Aref al-Aref ( ar, عارف العارف, 1892–1973), variously spelled as Arif el Arif, 'Arif el-'Arif, etc., was a Palestinian journalist, historian and politician. He served as mayor of East Jerusalem in the 1950s during the Jordanian annex ...
, Ibrahim Hashem
Ibrahim Hashem ( ar, إبراهيم هاشم; 1886 – 14 July 1958) was a Jordanian politician and judge, known primarily for serving five terms as Prime Minister. He died in Baghdad at the hands of a mob in front of the Iraqi Ministry of Defen ...
and Ahmed Hilmi Pasha
Ahmed Hilmi Abd al-Baqi ( ar, أحمد حلمي عبد الباقي 1883 - 1963) was a soldier, economist, and politician, who served in various post-Ottoman Empire governments, and was Prime Minister of the short-lived All-Palestine Government ...
), and the Jordanians described them as "military" governors, so that it would not anger the other Arab states, which opposed Jordan's plans to incorporate the Arab part of Palestine into the kingdom. The king made other smaller moves towards the annexation of the West Bank: He ordered Palestinian policemen to wear the uniforms of the Jordanian police and its symbols; he instituted the use of Jordanian postage stamp
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage (the cost involved in moving, insuring, or registering mail), who then affix the stamp to the f ...
s instead of the British ones; Palestinian municipalities were not allowed to collect taxes and issue licenses; and the radio of Ramallah called the locals to disobey the instructions of pro-Husseini
Husseini (also spelled Hussaini, Husaini, Hecini, Hosseini , Houssaini or Husayni, ar, حسیني) is an Arabic surname.
Etymology
It is a nisba derivation of the given name Hussein or Husain from the name of Imam Husain ibn Ali. People with the ...
officials and obey those of the Jordanian-backed governors.
The December 1948 Jericho Conference
The Jericho Conference ( ar, مؤتمر أريحا) was held in December 1948 to decide the future of the portion of Palestine that was held by Jordan at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, led by Sheikh Muhammad Ali Ja'abari. Pro-Jordanian p ...
, a meeting of prominent Palestinian leaders and King Abdullah I, voted in favor of annexation into what was then Transjordan. Transjordan became the ''Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan'' on 26 April 1949. Military occupation concluded on November 2, 1949 via promulgation of the Law Amending Public Administration Law in Palestine whereby the laws of Palestine were declared to remain applicable. In the Jordanian parliament, the West and East Banks received 30 seats each, having roughly equal populations. The first elections were held on 11 April 1950. Although the West Bank had not yet been annexed, its residents were permitted to vote.
Annexation
Jordan formally annexed the West Bank on 24 April 1950, giving all residents automatic Jordanian citizenship. West Bank residents had already received the right to claim Jordanian citizenship in December 1949. Unlike any other Arab country to which they fled after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Palestinian refugees in the West Bank (and on theEast Bank
Transjordan, the East Bank, or the Transjordanian Highlands ( ar, شرق الأردن), is the part of the Southern Levant east of the Jordan River, mostly contained in present-day Jordan.
The region, known as Transjordan, was controlled by nu ...
) were given Jordanian citizenship on the same basis as existing residents.
Jordan's annexation was widely regarded as illegal and void by the Arab League and others. Elihu Lauterpacht
Sir Elihu Lauterpacht (13 July 1928 – 8 February 2017) was a British academic and lawyer, who specialized in international law. The son of Sir Hersch Lauterpacht, he was founder of the Lauterpacht Centre for International Law at the Law Faculty ...
described it as a move that "entirely lacked legal justification." The annexation formed part of Jordan's "Greater Syria Plan" expansionist policy, and in response, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon and Syria joined Egypt in demanding Jordan's expulsion from the Arab League. A motion to expel Jordan from the League was prevented by the dissenting votes of Yemen and Iraq. On 12 June 1950, the Arab League declared the annexation was a temporary, practical measure and that Jordan was holding the territory as a "trustee" pending a future settlement. On 27 July 1953, King Hussein of Jordan
Hussein bin Talal ( ar, الحسين بن طلال, ''Al-Ḥusayn ibn Ṭalāl''; 14 November 1935 – 7 February 1999) was King of Jordan from 11 August 1952 until his death in 1999. As a member of the Hashemite dynasty, the royal family of ...
announced that East Jerusalem was "the alternative capital of the Hashemite Kingdom" and would form an "integral and inseparable part" of Jordan. In an address to parliament in Jerusalem in 1960, Hussein called the city the "second capital of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan".
Only the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
formally recognized the annexation of the West Bank, ''de facto'' in the case of East Jerusalem. In 1950, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
extended formal recognition to the union between the Hashemite Kingdom and that part of Palestine under Jordanian control - with the exception of Jerusalem. The British government stated that it regarded the provisions of the Anglo-Jordan Treaty of Alliance of 1948 as applicable to all the territory included in the union. The United States Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
also recognized this extension of Jordanian sovereignty.Joseph Massad said that the members of the Arab League granted de facto recognition and that the United States had formally recognized the annexation, except for Jerusalem. See Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
is claimed to have recognized Jordan's annexation too, but this is disputed. Despite Arab League opposition, the inhabitants of the West Bank became citizens of Jordan.
Tensions continued between Jordan and Israel through the early 1950s, with Palestinian guerrillas and Israeli commandos crossing the Green Line. Abdullah I of Jordan
AbdullahI bin Al-Hussein ( ar, عبد الله الأول بن الحسين, translit=Abd Allāh al-Awwal bin al-Husayn, 2 February 1882 – 20 July 1951) was the ruler of Jordan from 11 April 1921 until his assassination in 1951. He was the Emi ...
, who had become Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
of Transjordan in 1921 and King in 1923, was assassinated in July 1951 during a visit to the Jami Al-Aqsa on the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compou ...
in East Jerusalem by a Palestinian gunman following rumours that he was discussing a peace treaty with Israel. The trial found that this assassination had been planned by Colonel Abdullah el-Tell, ex-military governor of Jerusalem, and Musa Abdullah Husseini. He was succeeded by his son Talal and then his grandson Hussein
Hussein, Hussain, Hossein, Hossain, Huseyn, Husayn, Husein or Husain (; ar, حُسَيْن ), coming from the triconsonantal root Ḥ-S-i-N ( ar, ح س ی ن, link=no), is an Arabic name which is the diminutive of Hassan, meaning "good", " ...
.
Access to holy sites
Clauses in the 3 April 1949 Armistice Agreements specified that Israelis would have access to the religious sites in East Jerusalem. However, Jordan refused to implement this clause arguing that Israel's refusal to permit the return of Palestinians to their homes inWest Jerusalem
West Jerusalem or Western Jerusalem (, ; , ) refers to the section of Jerusalem that was controlled by Israel at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. As the city was divided by the Green Line (Israel's erstwhile border, established by t ...
voided that clause in the agreement. Tourists entering East Jerusalem had to present baptismal certificates or other proof they were not Jewish.
The special committee that was to make arrangements for visits to holy places was never formed and Israelis, irrespective of religion, were barred from entering the Old City and other holy sites. Significant parts of the Jewish Quarter, much of it severely damaged in the war, together with synagogue such as the Hurva Synagogue
The Hurva Synagogue ( he, בית הכנסת החורבה, translit: ''Beit ha-Knesset ha-Hurva'', lit. "The Ruin Synagogue"), also known as Hurvat Rabbi Yehudah he-Hasid ( he, חורבת רבי יהודה החסיד, "Ruin of Rabbi Judah the Piou ...
, which had also been used as a military base in the conflict, were destroyed. Collins (1973), pp. 492–94. and it was said that some gravestones from the Jewish Cemetery on the Mount of Olives
The Mount of Olives or Mount Olivet ( he, הַר הַזֵּיתִים, Har ha-Zeitim; ar, جبل الزيتون, Jabal az-Zaytūn; both lit. 'Mount of Olives'; in Arabic also , , 'the Mountain') is a mountain ridge east of and adjacent to Jeru ...
had been used to build latrines for a nearby Jordanian army barracks.
The Jordanians immediately expelled all the Jewish residents of East Jerusalem. All but one of the 35 synagogues in the Old City were destroyed over the course of the next 19 years, either razed or used as stables and chicken coops. Many other historic and religiously significant buildings were replaced by modern structures. The ancient Jewish cemetery on Mount of Olives
The Mount of Olives or Mount Olivet ( he, הַר הַזֵּיתִים, Har ha-Zeitim; ar, جبل الزيتون, Jabal az-Zaytūn; both lit. 'Mount of Olives'; in Arabic also , , 'the Mountain') is a mountain ridge east of and adjacent to Jeru ...
was desecrated, and the tombstones were used for construction, paving roads and lining latrines; the highway to the Intercontinental Hotel was built on top of the site.
Aftermath
Six-Day War and end of Jordanian control
By the end of theSix-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Ju ...
, the formerly Jordanian-controlled West Bank with its one million Palestinian population had come under Israeli military occupation
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
. About 300,000 Palestinian refugees were expelled or fled to Jordan. After 1967, all religious groups were granted administration over their own holy sites, while administration of the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compou ...
– sacred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims – remained in the hands of the Jerusalem Islamic Waqf
The Department of the Jerusalem Awqaf and Al-Aqsa Mosque Affairs, together with its board the Islamic Awqaf Council, is the Jordanian-appointed organization responsible for controlling and managing the current Islamic edifices on the Temple Moun ...
.
Jordanian disengagement
Jordanian disengagement from the West Bank (inArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
: قرار فك الارتباط), in which Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
surrendered the claim to sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
over the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, took place on 31 July 1988. On 31 July 1988, Jordan renounced its claims to the West Bank (with the exception of guardianship over the Muslim and Christian holy sites in Jerusalem), and recognized the Palestine Liberation Organization as "the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people."
Following the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Ju ...
in 1967, Israel occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
the West Bank (including East Jerusalem). Although the sides were technically at war, a policy known as "open bridges" meant that Jordan continued to pay salaries and pensions to civil servants and to provide services to endowments and educational affairs and in general to play an active role in West Bank affairs.
In 1972, King Hussein conceived a plan to establish a united Arab federation which would include the West Bank and Jordan. This proposal never came to fruition.
In 1974, the Arab League decided to recognize the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
. The decision forced King Hussein to relinquish his claim to speak for the Palestinian people during peace negotiations and to recognize an independent Palestinian state
Palestine ( ar, فلسطين, Filasṭīn), officially the State of Palestine ( ar, دولة فلسطين, Dawlat Filasṭīn, label=none), is a state located in Western Asia. Officially governed by the Palestine Liberation Organization ( ...
that is independent of Jordan.
On 28 July 1988, King Hussein announced the cessation of a $1.3 billion development program for the West Bank explaining that the aim of this move is to allow the PLO to take more responsibility for these territories. Two days later the king dissolved Jordan's lower house of parliament, half of whose members represented constituencies in the Israeli-occupied West Bank.
On 31 July 1988, King Hussein announced the severance of all legal and administrative ties with the West Bank, except for the Jordanian sponsorship of the Muslim and Christian holy sites in Jerusalem, and recognised the PLO's claim to the State of Palestine. In his speech to the nation held on that day he announced his decision and explained that this decision was made with the aim of helping the Palestinian people establishing their own independent state.
The 1993 Oslo Accords between the PLO and Israel "opened the road for Jordan to proceed on its own negotiating track with Israel." The Washington Declaration was initialled one day after the Oslo Accords were signed. "On July 25, 1994, King Hussein met with Israeli Prime Minister Rabin in the Rose Garden of the White House, where they signed the Washington Declaration, formally ending the 46-year state of war between Jordan and Israel." Finally, on 26 October 1994, Jordan signed the Israel–Jordan peace treaty
The Israel–Jordan peace treaty (formally the "Treaty of Peace Between the State of Israel and the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan"), he, הסכם השלום בין ישראל לירדן; transliterated: ''Heskem Ha-Shalom beyn Yisra'el Le-Yarden'' ...
, which normalized relations between the two countries and resolved territorial disputes between them.
Gallery
Porat Yosef Yeshiva
Porat Yosef Yeshiva ( he, ישיבת פורת יוסף) is a Sephardic yeshiva in Jerusalem, with locations in both the Old City and the Geula neighborhood. The name Porat Yosef means "Joseph is a fruitful tree" after the biblical verse Genesi ...
, Old City of Jerusalem, 1948
File:King Abdullah, Jerusalem, 29 May 1948.jpg, King Abdullah at Church of the Holy Sepulchre, 29 May 1948
File:Arab Legion soldier in ruins of Hurva.jpg, Arab Legion soldier posing in the ruins of the Hurva Synagogue
The Hurva Synagogue ( he, בית הכנסת החורבה, translit: ''Beit ha-Knesset ha-Hurva'', lit. "The Ruin Synagogue"), also known as Hurvat Rabbi Yehudah he-Hasid ( he, חורבת רבי יהודה החסיד, "Ruin of Rabbi Judah the Piou ...
, Jerusalem
File:UKrecognizesIsraelJordan.pdf, Announcement in the UK House of Commons
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England.
The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 mem ...
of the recognition of the State of Israel and also of the annexation of the West Bank by the State of Jordan
See also
*List of East Jerusalem locations
This is a list of locations in Jerusalem sometimes described by the term ''East Jerusalem'':
Locations in Jordanian municipality (1949–1967)
The following locations were included within the borders of the Jordanian municipality in the easter ...
* List of military occupations
This article presents a list of military occupations. Only military occupations since the customary laws of belligerent military occupation were first clarified and supplemented by the Hague Convention of 1907 are included In this article.
Mili ...
* Military occupation
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
* Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt
The occupation of the Gaza Strip by the United Arab Republic refers to the time period in which the present-day Palestinian territory known as the Gaza Strip was occupied by Egyptian forces of the United Arab Republic from 1949 to 1967. The ...
* Israeli occupation of the West Bank
The Israeli occupation of the West Bank began on 7 June 1967, when Israeli forces captured and occupied the territory (including East Jerusalem), then occupied by Jordan, during the Six-Day War, and continues to the present day. The status of ...
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * *Further reading
* * * * *Hussein Move May Snag Peace Initiative
- published on
Palm Beach Post
''The Palm Beach Post'' is an American daily newspaper serving Palm Beach County in South Florida, and parts of the Treasure Coast. On March 18, 2018, in a deal worth US$42.35 million, ''The Palm Beach Post'' and ''The Palm Beach Daily News'' we ...
on July 31, 1988
Hussein Muddies Mideast Waters
- published on
Milwaukee Journal
The ''Milwaukee Journal Sentinel'' is a daily morning broadsheet printed in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, where it is the primary newspaper. It is also the largest newspaper in the state of Wisconsin, where it is widely distributed. It is currently o ...
on August 1, 1988
King Hussein's Bombshell
- published on
Pittsburgh Press
''The Pittsburgh Press'' (formerly ''The Pittsburg Press'' and originally ''The Evening Penny Press'') was a major afternoon daily newspaper published in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, from 1884 to 1992. At one time, the ''Press'' was the second larg ...
on August 4, 1988
External links
Disengagement from the West Bank
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jordanian occupation of the West Bank History of Palestine (region) 20th century in Jerusalem Israel–Jordan relations Military occupation Annexation of the West Bank Annexation of the West Bank Annexation of the West Bank States and territories established in 1948 States and territories disestablished in 1967 Annexation of the West Bank Annexation of the West Bank History of the West Bank West Bank Governorate 1988 in Jordan Palestine Liberation Organization Israeli–Palestinian conflict Arab–Israeli conflict July 1988 events in Asia 1940s in the West Bank Governorate 1950s in the West Bank Governorate 1960s in the West Bank Governorate 1940s in Jerusalem 1950s in Jerusalem 1960s in Jerusalem Annexation